When I first learned about the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA), I’ll admit I felt a bit overwhelmed.
As someone who’s managed WordPress sites for many years, the idea of learning yet another privacy law felt like a lot. But when I dug into it, I realized it’s more straightforward than it looks.
Still, I’ve seen plenty of site owners make compliance harder than it needs to be—either by overcomplicating the process or missing simple steps.
That’s why I created this guide. I’ll walk you through the VCDPA’s core requirements step by step and share the tools I use to improve WordPress compliance without getting overwhelmed by legal jargon.
What is the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)?
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) is a state privacy law that gives Virginia residents more control over their personal data. This includes information that can identify someone directly or indirectly—like names, email addresses, IP addresses, or data collected through website forms or tracking tools.
Even if your business isn’t based in Virginia, the VCDPA might still apply to your WordPress site. What matters is whether you collect personal data from Virginia residents.
That said, the law doesn’t apply to every site. It’s mainly aimed at larger businesses and organizations.
Generally, you need to comply with the VCDPA if you:
- Control or process the personal data of 100,000 or more Virginia consumers in a calendar year, or
- Control or process the personal data of at least 25,000 Virginia consumers and get over 50% of your total revenue from selling personal data.
Keep in mind that the law also only applies to businesses or organizations operating for commercial purposes.
If your site fits one of those categories, then it’s essential to understand how the VCDPA works and what steps you need to take to stay compliant.
Why Should WordPress Users Care About VCDPA Compliance?
If your WordPress site falls under the VCDPA, then staying compliant helps you avoid potential penalties. The Virginia Attorney General enforces the VCDPA, and violations can lead to fines of up to $7,500 per incident.
Fortunately, you’ll usually receive a 30-day warning and a chance to fix the issue before any penalties are applied.
It’s also worth noting that consumers can’t directly sue you under this law. Only the Attorney General can take action, which adds a layer of protection, but doesn’t mean you should ignore compliance.
More importantly, showing that you care about user privacy helps build trust with your audience.
When visitors know you’re being transparent and responsible with their data, they’re more likely to stick around, sign up for your email newsletter, or make a purchase from your online store.
Simply put, staying compliant is not just a legal duty. It’s also a key part of building trust and achieving long-term success.
How VCDPA Affects Your WordPress Site
If your site is covered by the VCDPA, then you’re required to support several privacy rights for your visitors. That means making it easy for Virginia residents to control how their personal data is collected, used, and deleted.
As a WordPress site owner, here are the main rights you need to understand and support:
- The Right to Know: Visitors can ask what personal data you’ve collected about them.
- The Right to Correction: They can request that you fix any incorrect or outdated information.
- The Right to Opt-Out: Users can ask you not to sell or share their personal data with other companies.
- The Right to Data Portability: They can request a copy of their personal data in a format they can use elsewhere, like a ZIP file.
- The Right to Delete: Users can ask you to permanently delete the data you’ve collected about them.
Throughout this guide, I’ll show you how to support each of these rights using WordPress tools and beginner-friendly strategies.
How to Improve Your VCDPA Compliance in WordPress
VCDPA compliance may sound technical. But at its core, it’s about being transparent with your visitors and giving them control over their personal data.
As a WordPress site owner, there are practical steps you can take to meet these requirements. These include limiting how much data you collect, creating clear policies, and making it easy for users to opt out or request changes.
In this article, I will walk you through each part of the process. You can follow them step-by-step or jump to the parts that apply to your site using the links below:
- Perform a Data Audit
- Create a Data Compliance Record
- Collect Less Data
- Create a Privacy Policy
- Add a Cookie Popup
- Write a Separate Cookie Policy
- Block Third-Party Scripts
- Track and Log Visitor Consent
- Provide an Easy Opt-Out for Data Sales
- Support the ‘Right to Delete’
- Handle Data Access Requests Efficiently
- Support the ‘Right to Correction’
- FAQs About VCDPA Compliance in WordPress
- Additional Resources for Privacy Compliance
Perform a Data Audit
The first step to VCDPA compliance is understanding how your website collects and stores personal data. That means reviewing the tools, plugins, and services you use—and documenting the information they gather.
To start, I recommend making a list of every WordPress plugin on your site, along with any third-party tools that interact with user data. This could include analytics platforms, form builders, or SEO tools.
Once you have that list, check what kind of personal information each tool collects. For example, if you’ve added a quote request form, you’ll want to record whether it asks for names, company details, or job titles.
To guide your audit, ask yourself:
- What personal data do I collect? This includes names, email addresses, IP addresses, payment details, and any other data submitted through forms or comments.
- Where is this data stored? Is it saved on your own server or sent to an outside service?
- Why am I collecting this information? The VCDPA says data must be “adequate, relevant, and reasonably necessary” for your stated purpose.
- How long do I keep it? You should only store personal data as long as it’s needed for its original purpose.
- Do I share this data with anyone? This includes service providers, third-party tools, or advertising networks. Be sure to note whether any of this data is used for targeted ads.
Once you’ve completed your audit, you’ll have a clear picture of what data you collect, where it’s stored, and what you need to adjust to meet VCDPA requirements.
Create a Data Compliance Record
After completing your data audit, the next step is to keep a written record of what you found. This document should explain the actions you’ve already taken to follow the VCDPA, along with any updates or fixes you made during your audit.
By creating this record, you’ll have clear proof that you take privacy seriously. That can be helpful if you’re ever audited or if someone asks about your compliance practices.
As you’ll see throughout this guide, it’s not enough to follow the VCDPA behind the scenes. You also need to be able to show that you’re doing things the right way.
Every business website is different, but I recommend running a new data audit and updating your records at least once per year.
You should also update your records any time you change how your site collects or uses personal data. For example, after installing a new plugin that collects user info, or when the law itself changes, it’s a good time to revisit your audit and notes.
Keeping this record up to date doesn’t take much time, and it’ll make compliance much easier in the long run.
Collect Less Data
The VCDPA says you should only collect personal data that’s “adequate, relevant, and reasonably necessary” to meet a specific goal.
In other words: don’t collect anything you don’t truly need.
This idea is known as data minimization. It means reviewing what you currently collect and looking for ways to reduce it. If a piece of information isn’t essential for your site to function—or for the task at hand—it’s better to leave it out.
After completing your data audit, carefully review all the information you collect. Ask yourself: “Do I truly need every single piece of information I’m asking for?”
If something isn’t necessary, remove it. The less data you collect, the easier it is to stay compliant, and the less you’ll have to manage when users make requests.
This approach also builds trust. By avoiding unnecessary questions, you show that you respect your visitors’ privacy and value their time.
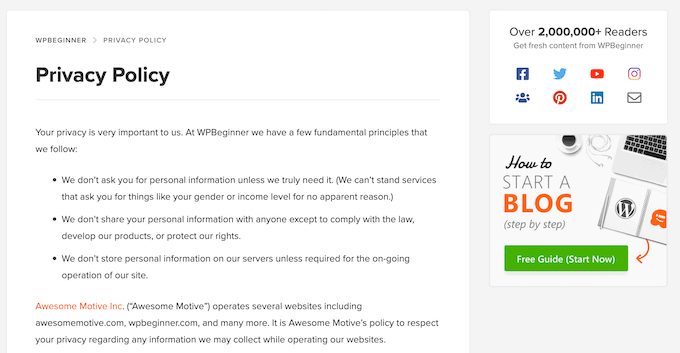
Create a Privacy Policy
A privacy policy is a page on your website that clearly explains what personal data you collect, how you use it, and who you share it with.
Having a clear, up-to-date privacy policy is essential for VCDPA compliance. It helps visitors understand how their information is handled and directly supports the VCDPA’s Right to Know requirement.
To make things easier, WordPress includes a built-in tool for creating a privacy policy. You can find it by going to Settings » Privacy in your WordPress dashboard.

Alternatively, you can use our own WPBeginner privacy policy page as a starting point.
Just remember to change all mentions of ‘WPBeginner’ to your specific business or website name.
Want more detailed instructions? We also have a complete, step-by-step guide on how to add a privacy policy in WordPress.
If your site already has a privacy policy, that’s great, but you’ll still need to review and update it to reflect the VCDPA.
In particular, make sure it covers the key rights your visitors have:
- Right to Know
- Right to Delete
- Right to Correction
- Right to Opt Out
You’ll also need to explain how users can act on those rights. For example, you might link to a contact form where visitors can request access to their data, or provide steps for updating their profile information.
Finally, don’t forget to keep your privacy policy up to date. This ensures it always reflects your current data practices and any changes to the VCDPA.
Add a Cookie Popup
Many websites use cookies to track user behavior, display ads, or measure analytics. If your site does this, the VCDPA expects you to inform users and give them a way to opt out.
Unlike the GDPR, which requires visitors to actively agree before data is collected, the VCDPA follows an opt-out model. That means you can often collect data by default—as long as users are told what’s being collected and can say no if they want to.
One of the simplest ways to meet this requirement is by adding a cookie popup. A good popup should explain what types of cookies your site uses, what data is being collected, and how that information is used. It should also give users a clear way to opt out.
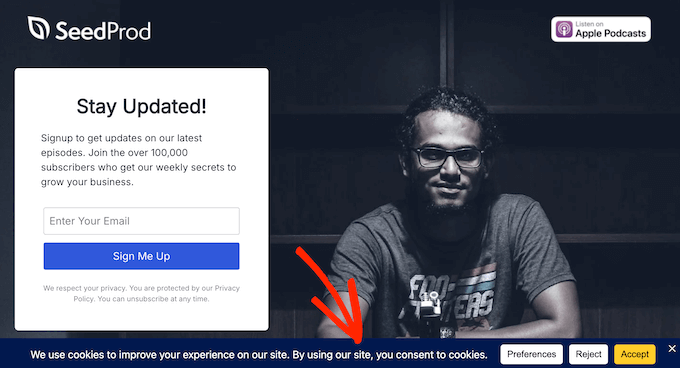
I recommend using WPConsent for this. It’s the same plugin we use on WPBeginner to manage cookie banners and user consent.
It works well for WordPress beginners and is actively updated to follow privacy laws like the VCDPA, GDPR, and CCPA.
💡Want to know more about how WPConsent works on our site? Our in-depth WPConsent review has all the details.

You can also find a free version of WPConsent in the WordPress plugin directory.
To get started, simply install and activate the plugin.
After you activate it, WPConsent will automatically scan your site for active cookies. It will then record all the cookies it finds.
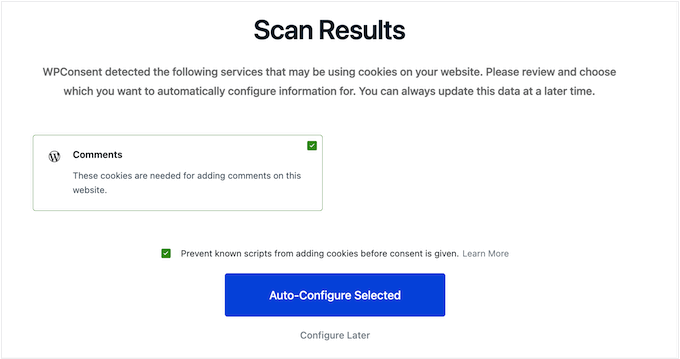
Next, WPConsent’s setup wizard will help you change how your cookie popup looks. You can adjust the layout, the text size, button styles, colors, and even add your own custom logo.
As you make changes, WPConsent will show a live preview. This lets you see exactly how the banner will look on your WordPress website.
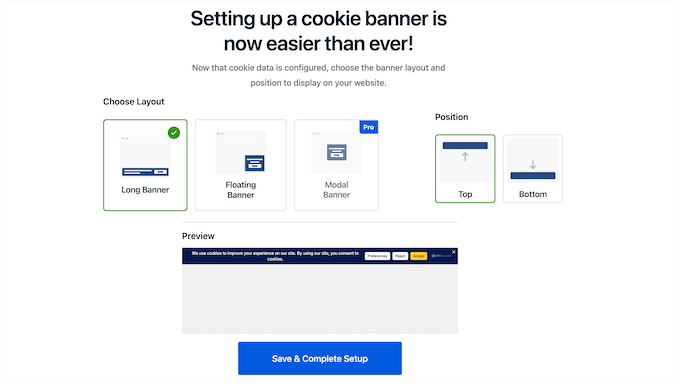
When you’re happy with how everything is set up, just save your changes. The cookie banner will then appear on your WordPress website, helping you comply with the VCDPA.
For more detailed instructions, see our full guide on how to add a cookie popup in WordPress.
Write a Separate Cookie Policy
A cookie popup is a good starting point, but it’s also smart to create a dedicated cookie policy.
This separate page gives visitors more detail about how your site uses cookies. That way, they can better understand what personal information you collect and how it’s used.
In your cookie policy, you should list all the different types of cookies you use on your site. For example, you might use essential cookies (required for your site to work), analytics cookies (to measure website traffic), or marketing cookies (for advertising).
You should also explain what each type of cookie does. For example, some cookies might track user behavior or deliver targeted ads.
It’s also a good idea to describe what kinds of personal data each cookie collects. This might include a visitor’s IP address, device type, or browsing activity.
To build trust, keep your cookie policy easy to understand. This means you should avoid technical terms or legal words that are hard to follow. Instead, use clear and direct language that anyone can read.
Once your cookie policy is written, make sure it’s easy to find. I recommend linking to it from your footer and your cookie popup, as well as your main privacy policy.
Luckily, a tool like WPConsent can do much of this for you.
As you saw earlier, when you first install WPConsent, it automatically scans your site and identifies any active cookies.
To do this, go to WPConsent » Settings.
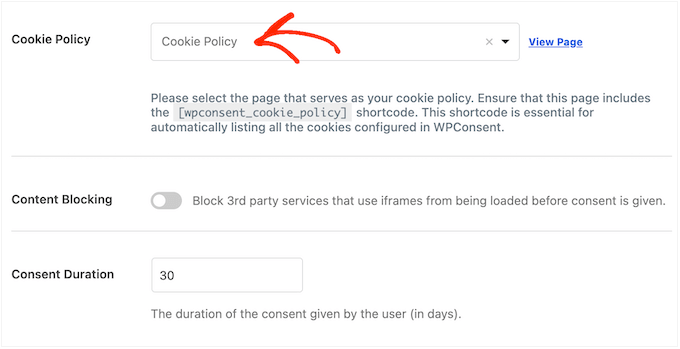
In the plugin’s settings, choose the page where you want to display the cookie policy.
WPConsent will then add this policy to your chosen page. It’s that simple.

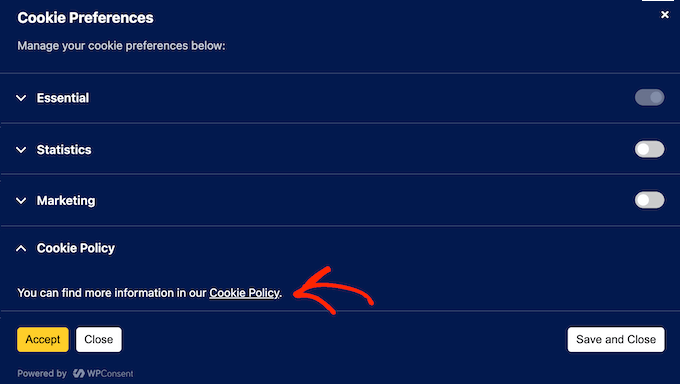
If you’re using WPConsent to display a cookie popup, then visitors can now access this policy directly from the popup itself.
They just need to select the ‘Preferences’ button.
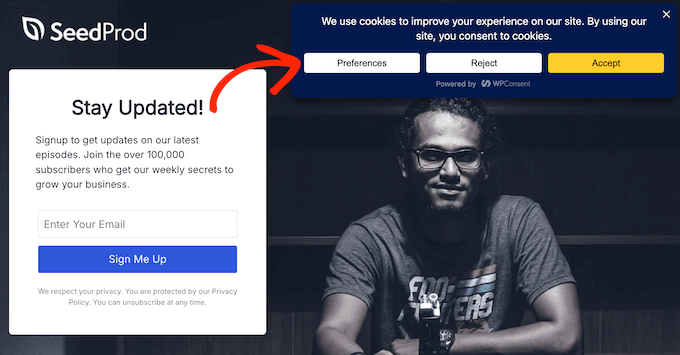
From there, they can click the ‘Cookie Policy’ link.
WPConsent will then take them straight to the correct page.
Block Third-Party Scripts
One of the most challenging things about VCDPA compliance is that it also covers external tracking tools. These include popular services like Google Analytics and Facebook Pixel.
The reason for this is simple: these tracking tools often collect visitor data. Under the VCDPA, you’re responsible for managing how these third-party tools collect, store, and use that personal information.
You also need to give visitors a way to stop these tools from tracking them if they choose.
So, how do you control tracking scripts from other companies? There’s an easy answer: automatic script blocking.
The VCDPA generally allows the use of tracking tools unless a visitor opts out, especially when used for targeted advertising. But a best practice for building user trust is to block tracking scripts until the visitor opts in.
This approach goes beyond VCDPA requirements and also helps you comply with stricter laws like GDPR. With this feature, scripts won’t load until the visitor explicitly agrees.
It also provides visitors with the information they need to understand what they’re agreeing to before you collect any data. This helps you meet the VCDPA’s Right to Know rule.
Plus, you’re getting a head start on complying with other privacy laws like Europe’s GDPR, which does require opt-in consent. It’s a great way to make your website’s privacy practices strong all around.
Fortunately, WPConsent has an automatic script blocking feature that works out of the box.
Simply activate the plugin, and it will find and block common tracking scripts automatically. This includes tools like Google Analytics, Google Ads, and Facebook Pixel. Even better, WPConsent does this without breaking your site.
As soon as a visitor gives their consent, WPConsent will run the blocked script. This provides a very smooth user experience because the page does not need to reload.
Track and Log Visitor Consent
Even if you follow all the VCDPA rules, regulators might still question how you handle data or even audit your site.
If this happens, you’ll need to prove that you’re respecting your audience’s choices. That’s why it’s important to keep a detailed record of user consent.
WPConsent makes this easy by automatically logging each user’s consent. It saves all the important details, including the user’s IP address, their consent choices, and the exact date and time they made those choices.
You can see this information at any time by going to WPConsent » Consent Logs in your WordPress dashboard.
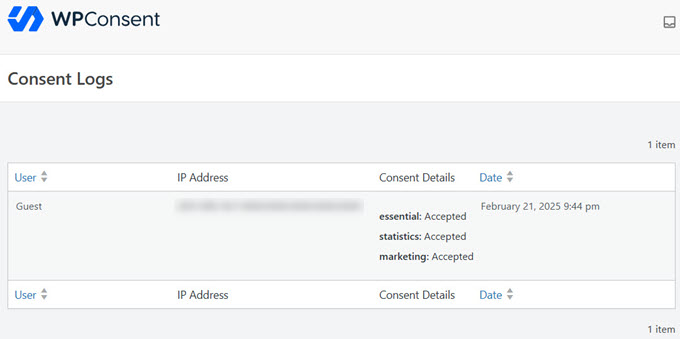
Need to share this information with an auditor or team member? You can export it from your WordPress dashboard in just a few clicks.
To do this, just click the ‘Export’ tab. Then, enter the ‘From Date’ and ‘To Date’ for the export. This creates a CSV file, ready for you to share with auditors, customers, and anyone else who needs access.
Provide an Easy Opt-Out for Data Sales
Under the VCDPA, if your site sells or shares personal data, then you must give visitors a way to opt out.
The easiest way to do this in WordPress is with WPConsent’s Do Not Track add-on. Despite its name, it gives you exactly what you need to meet the VCDPA’s opt-out of sale requirement.
To get started, go to WPConsent » Do Not Track » Configuration inside your WordPress dashboard.
WPConsent will then guide you through the steps to install this add-on and create a ‘Do Not Track’ form.
🌟 Want more detailed instructions? Then see our guide on how to create a Do Not Sell My Info page in WordPress.
Once it’s active, visitors can fill out a simple form to opt out of the sale or sharing of their data.
Even better, WPConsent stores all opt-out requests directly on your website in a secure table. That way, you keep full control over sensitive data instead of depending on external services.
It also logs each request automatically, giving you built-in proof of compliance in case of an audit.
Support the ‘Right to Delete’
As I mentioned earlier, the VCDPA gives users the right to ask you to delete their personal data.
There are different ways to handle these requests, but the easiest is to add a ‘data erasure’ form to your site.
This is where WPForms can help. It’s a user-friendly form builder that lets you create all kinds of forms using a drag-and-drop editor.
🌟 Here at WPBeginner, we’re not just recommending WPForms – we built all our own forms with it!
From our contact pages to our surveys, it’s all powered by WPForms. We use it daily, which is why we’re confident recommending it.
Ready to see why it’s our go-to? Dive into our detailed WPForms review.
When it comes to fulfilling the VCDPA’s ‘Right to Delete’, WPForms comes with a ready-made Right to Erasure Request Form template.
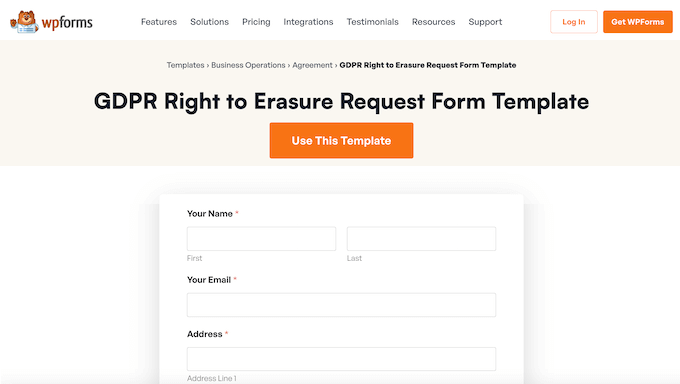
This provides a strong starting point, so you can add this important form to your site quickly and easily.
After installing WPForms, you can customize the Right to Erasure Request Form template in a user-friendly editor. This makes it easy to add, remove, and change the default fields.
When you’re happy with how the form is set up, you can add it to your site using either a shortcode or the WPForms block.

Finally, you’ll want to make sure visitors can find this form easily. I recommend linking to it from your privacy policy or even embedding the form directly on your privacy policy page.
WPForms also includes an entry management system that lets you filter form submissions and act on new deletion requests right away.
To review your entries, go to WPForms » Entries in the WordPress dashboard.
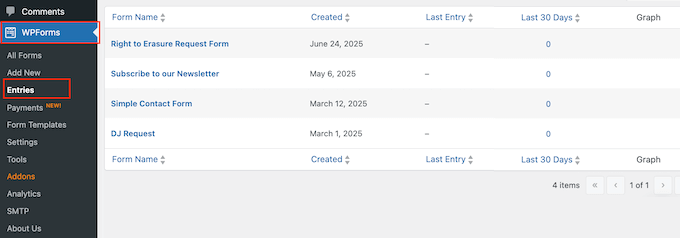
You’ll now see all the different forms you’ve created. Simply find the data erasure form and give it a click.
WPForms will now display all your ‘delete data’ requests.
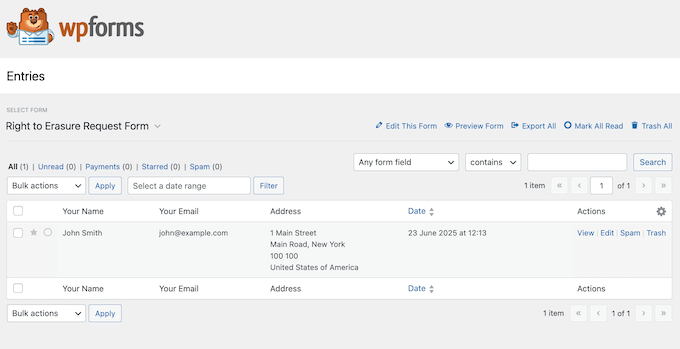
To process these requests, you can use WordPress’s built-in ‘Erase Personal Data’ tool, which lets you delete user information with just a few clicks.
To begin, go to Tools » Erase Personal Data.
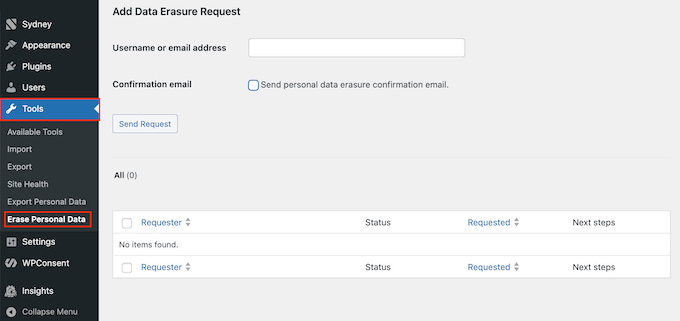
In the ‘Username or email address’ field, type in the user’s name or email.
This tool also has a ‘Send personal data erasure confirmation email’ setting. You can use it to let the user know you’ve deleted their data.
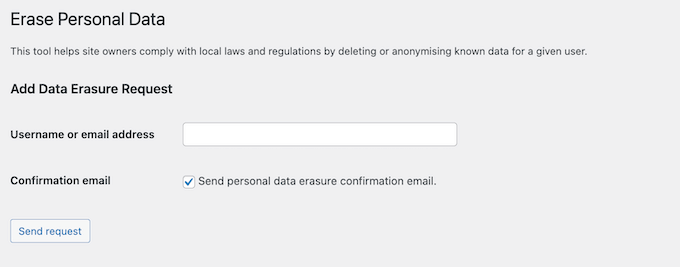
For full VCDPA compliance, you’ll also need to delete this data from any other tools or services where it’s stored.
By creating this clear process, you are making it easy for users to exercise their ‘Right to Delete,’ which is a core part of VCDPA compliance.
Handle Data Access Requests Efficiently
Under the VCDPA, visitors have two related rights: the right to access their data and the Right to Data Portability. This means they can request a copy of their personal data in a format that’s easy to use.
The good news is you can handle these requests the same way you manage data deletion.
To start, you can add a data access form to your site using WPForms. It includes a ready-made Data Request template designed to collect all the information needed to identify the user in your records.
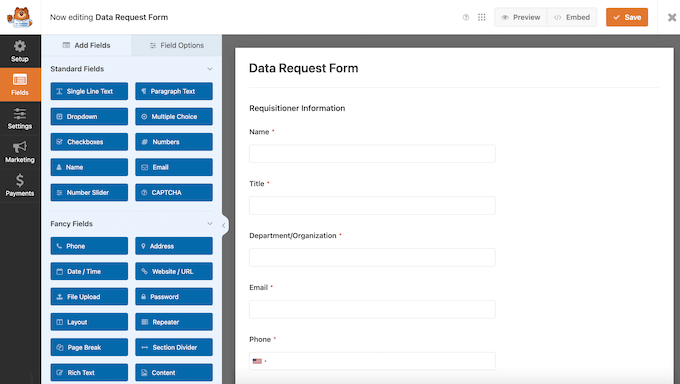
After adding this form to your site, WPForms will automatically record and show all access requests directly in your WordPress dashboard.
That way, you can view and respond to new requests as they arrive.
To review these requests, just go to WPForms » Entries.

Here, select your data request form. WPForms will then show all the entries for this form.
WordPress also includes a built-in Export Personal Data tool. You can use this to get all known data for any user, conveniently packaged as a .zip file.
To create this file, go to Tools » Export Personal Data in your WordPress dashboard.
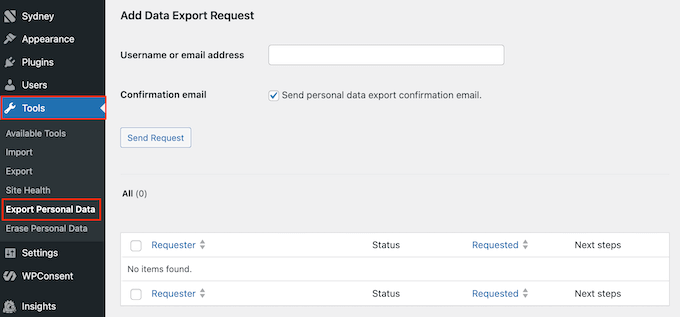
You can then type in the person’s username or email address to find the correct record.
Then, simply share the .zip file with the person who made the request.
Support the ‘Right to Correction’
Under the VCDPA, people can ask you to correct or update their personal data if it’s wrong or incomplete.
This might happen after a user requests and reviews a copy of their personal data. Or, some visitors may contact you directly if their information changes.
For example, they might move to a new address, get a new phone number, or want to update other details they previously shared with you.
As with the other user rights, the easiest way to comply with the VCDPA is by adding a form to your site. And once again, WPForms has a ready-made template designed for this exact task.
The Personal Information Form Template comes with a built-in ‘Update Existing Record’ checkbox. Users can check this box to show they’re sending information to update a profile you already have for them.
This means you’ll immediately know why the user submitted this form.
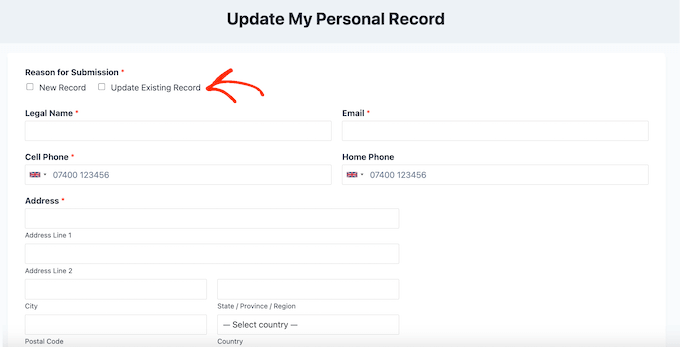
This template comes with many essential fields already included, such as legal name, preferred nickname, email address, home phone, and cell phone.
However, every website stores different kinds of information, so you may need to customize the form to collect additional details.
In that case, you can simply open the template in the WPForms editor. Here, you can add more fields to the form using simple drag-and-drop.
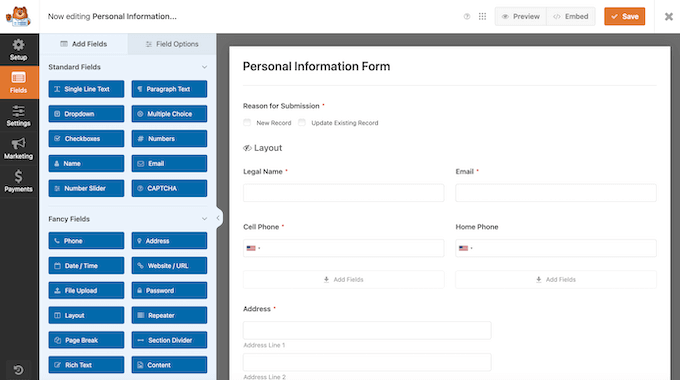
You can then fine-tune these fields using the left-hand panel. Just repeat these steps until the form collects all the information your users might want to edit.
With that done, you can publish the form on your site as normal.
Don’t forget to make your correction form easy to find on your site. I recommend adding a link in important places, such as your website’s footer or privacy policy.
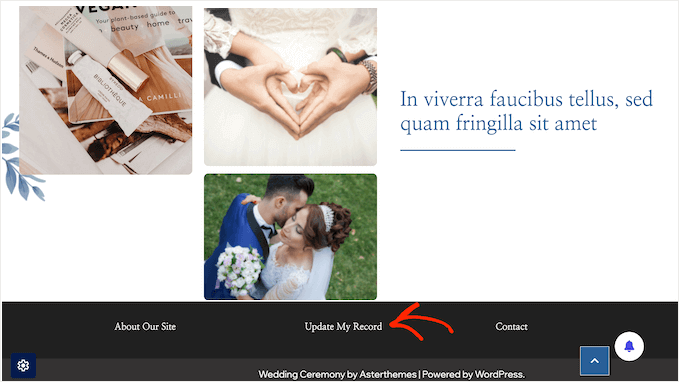
Remember that WPForms shows all form entries directly in your WordPress dashboard. This makes it easy to spot data correction requests as they come in.
How you update a user’s information will depend on the tools and software your site uses. For example, you might need to update a record inside your customer relationship management (CRM) app or email management software.
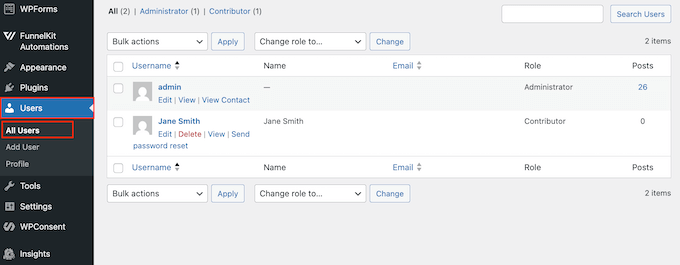
If the data is stored directly in WordPress, go to Users » All Users in your dashboard.
Here, find the user profile you need to update and click its ‘Edit’ link.
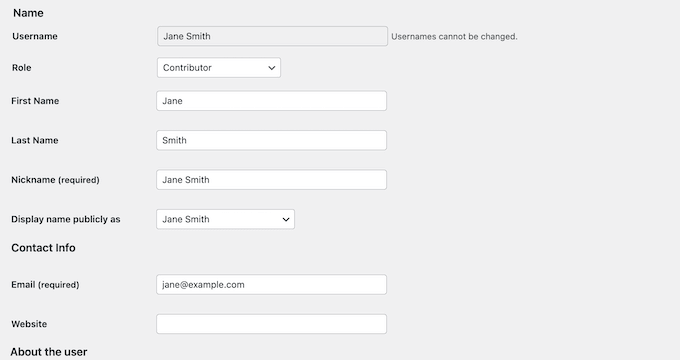
You will now see all the essential information WordPress has stored for that user.
From here, you can make any necessary changes and then save the user’s updated profile.
FAQs About VCDPA Compliance in WordPress
VCDPA compliance can seem overwhelming at first, but it doesn’t have to be.
To help you out, here are some of the most common VCDPA questions we hear at WPBeginner.
These answers cover the key parts of VCDPA compliance, clear up common concerns, and show you how to stay on the right side of the law.
What Is VCDPA and How Does It Affect My WordPress Site?
The VCDPA is a privacy law that gives Virginia residents more control over their personal data.
If your WordPress site handles personal data of Virginia residents and meets certain thresholds (such as processing the data of 100,000 or more consumers), then you must follow the VCDPA in order to avoid penalties.
How Does VCDPA Differ From GDPR?
Both the VCDPA and GDPR focus on protecting personal data. However, the VCDPA applies specifically to residents of Virginia.
It also has some unique rules not found in GDPR. For example, VCDPA generally uses an ‘opt-out’ approach for most data collection. This means you can collect data unless a user specifically tells you not to.
Meanwhile, the GDPR typically requires an opt-in, which means you need to get the user’s clear agreement before collecting their data.
That’s why it’s important to understand which privacy laws apply to your site.
What Should I Do If I Receive a Data Request (Like a Right to Delete Request)?
If you get a request from a Virginia resident to access, delete, or correct their personal data, you must respond as soon as possible, but in all cases within 45 days.
This period may be extended once by another 45 days when reasonably necessary, as long as you inform the consumer within the first 45-day window.
This means confirming the request, providing the requested data, and taking the correct action, like deleting that data.
Since you’re on a deadline, it’s important to have a clear process for handling these requests.
How Do Small Websites Handle VCDPA Compliance?
Smaller websites may need to comply if they meet the VCDPA thresholds for processing Virginia consumer data. This means they:
- Process the personal data of 100,000 or more Virginia consumers in a year, OR
- Process data of at least 25,000 consumers and get over 50% of their total income from selling that data.
If your site qualifies, here’s how you can start working toward compliance:
- Setting up plugins to help with privacy management, such as cookie consent tools and form plugins for collecting data requests.
- Avoid collecting unnecessary data, and stick to data minimization.
- Ensure all data collection methods follow the VCDPA rules.
- Keep your privacy and cookie policies up to date so they reflect your current practices.
Even if you’re running a smaller site, having the right tools and processes in place can make VCDPA compliance much easier and help you build trust with your audience along the way.
Additional Resources for Privacy Compliance
Complying with privacy laws isn’t a one-time task. You’ll need to continue learning and working on your site to remain in line with the law.
With that said, here are some resources to help you on that journey:
- How to Add a Privacy Policy in WordPress – This guide shows you how to create a privacy policy that meets VCDPA standards. You’ll also find tools and templates that you can use to create a privacy policy that covers all legal requirements.
- Best WordPress Security Plugins to Protect Your Site – Our top pick of the best plugins for keeping users and their personal information safe.
- Beginner’s Guide to PDPL Compliance – Do some of your visitors or users live in Saudi Arabia? If so, then you need to comply with another important privacy law: the Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL).
- The Ultimate Guide to WordPress and CCPA Compliance – While the CCPA shares some goals with VCDPA, it has different requirements for businesses and consumer rights. This guide has all the information you need to understand those differences.
- UCPA Compliance in WordPress: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide – This resource helps you understand the Utah Consumer Privacy Act (UCPA) and how it differs from the VCDPA.
I hope this beginner’s guide to VCDPA compliance for WordPress websites has helped you understand this important privacy law. Next, you may want to see our expert picks for the best GDPR plugins to improve compliance, or see our guide on how to keep personally identifiable info out of Google Analytics.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.
The post Beginner’s Guide to VCDPA Compliance in WordPress first appeared on WPBeginner.
Dr Crash says: